| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
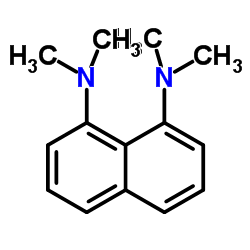 |
1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene
CAS:20734-58-1 |
|
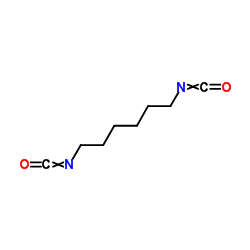 |
1,6-Diisocyanatohexane
CAS:822-06-0 |