Free radicals and their interpretations.
T Jávor, T Past, L Nagy, G Mózsik, I Wittmann
Index: Acta Physiol. Hung. 73(2-3) , 323-30, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Oxygen free radicals can be blamed for evoking gastric mucosal damage, because of the protective effect of some lipid soluble free radical scavengers (vitamin A related compounds, Vitamin E). Direct determination of free oxygen radicals related chemical entities in the gastric tissue during ulcerogenesis yielded controversial results. Aluminum antacid compound together with acid binding property exhibited cytoprotection too, elevating the tissue PGE2 level substantially. Magnesium containing antacid according to our model experiments on red blood cells damage by free radicals, is capable to bind free radicals as well as to counteract with the dangerous intracellular calcium accumulation. It has been concluded that aluminum-magnesium antacid has a cytoprotective effect via: 1. acid binding; 2. prostaglandin generation; 3. free radical scavenging; 4. calcium antagonist activity.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
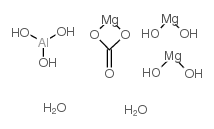 |
Almagate
CAS:66827-12-1 |
CH11AlMg3O12 |
|
[A method of increasing the effectiveness of anti-ulcer ther...
1989-10-01 [Klin. Med. (Mosk.) 67(10) , 66-8, (1989)] |
|
Effects of effervescent ranitidine on gastric pH: comparison...
2004-09-15 [Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 20(6) , 683-8, (2004)] |
|
Antacid (A02A) and antiulcer (A02B) drug prescription patter...
1998-06-01 [Eur. J. Epidemiol. 14(4) , 363-72, (1998)] |
|
Scrub typhus meningoencephalitis occurring during doxycyclin...
2011-03-01 [Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 69(3) , 271-4, (2011)] |
|
Protection by almagate of ethanol-induced gastric mucosal da...
1995-02-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 47(2) , 128-30, (1995)] |