Sensitive and selective fluorescence determination of trace hydrazine in aqueous solution utilizing 5-chlorosalicylaldehyde.
Xiaotong Chen, Yu Xiang, Zifan Li, Aijun Tong
Index: Anal. Chim. Acta 625(1) , 41-6, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A facile fluorescent method for the determination of hydrazine in aqueous solution with excellent sensitivity was developed. 5-chlorosalicylaldehyde (CS), a readily commercially available compound, was applied as the derivatization reagent in this work. Under the addition of CS to hydrazine aqueous solution (ethanol/water/acetic acid=30/66/4), an intense fluorescence enhancement was observed at 570 nm with a large stokes shift of approximately 170 nm. Upon the optimal condition, the fluorescence intensity linearly increased with the concentration of hydrazine in the range of 0.2 and 9.3 microM with a correlation coefficient of R2=0.9995 (n=10) and a detection limit of 0.08 microM. The R.S.D. was 2.0% (n=5). Determination of hydrazine in river and drinking water samples was successfully performed. Hydrazine vapor sensing by the proposed method was also reported.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
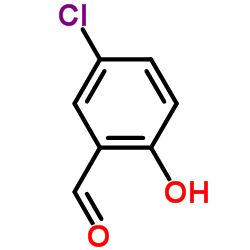 |
5-Chloro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde
CAS:635-93-8 |
C7H5ClO2 |
|
Palladium(0)-mediated C-H bond activation of N-(naphthyl)sal...
2015-08-14 [Dalton Trans. 44 , 13615-32, (2015)] |
|
Structural, spectroscopic and DFT study of 4-methoxybenzohyd...
2015-02-25 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 137 , 692-700, (2015)] |
|
New ruthenium(II) carbonyl complexes bearing disulfide Schif...
2014-08-14 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 129 , 352-8, (2014)] |
|
A planar Schiff base platinum(II) complex: crystal structure...
2014-01-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 62(3) , 221-8, (2014)] |