Celastrol ameliorates HIV-1 Tat-induced inflammatory responses via NF-kappaB and AP-1 inhibition and heme oxygenase-1 induction in astrocytes.
Gi Soo Youn, Dong-Joo Kwon, Sung Mi Ju, Hyangshuk Rhim, Yong Soo Bae, Soo Young Choi, Jinseu Park
Index: Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 280(1) , 42-52, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
HIV-1 Tat causes extensive neuroinflammation that may progress to AIDS-related encephalitis and dementia. Celastrol possesses various biological activities such as anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, and anti-inflammatory activities. In this study, we investigated the modulatory effects of celastrol on HIV-1 Tat-induced inflammatory responses and the molecular mechanisms underlying its action in astrocytes. Pre-treatment of CRT-MG human astroglioma cells with celastrol significantly inhibited HIV-1 Tat-induced expression of ICAM-1/VCAM-1 and subsequent monocyte adhesiveness in CRT-MG cells. In addition, celastrol suppressed HIV-1 Tat-induced expression of pro-inflammatory chemokines, such as CXCL10, IL-8, and MCP-1. Celastrol decreased HIV-1 Tat-induced activation of JNK MAPK, AP-1, and NF-κB. Furthermore, celastrol induced mRNA and protein expression of HO-1 as well as Nrf2 activation. Blockage of HO-1 expression using siRNA reversed the inhibitory effect of celastrol on HIV-1 Tat-induced inflammatory responses. These results suggest that celastrol has regulatory effects on HIV-1 Tat-induced inflammatory responses by blocking the JNK MAPK-AP-1/NF-κB signaling pathways and inducing HO-1 expression in astrocytes. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
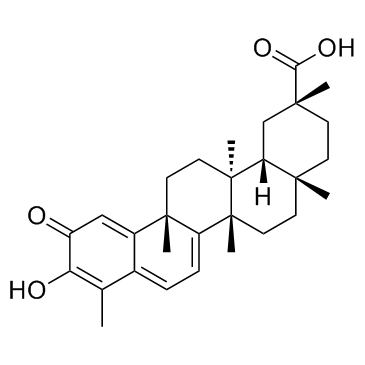 |
Celastrol
CAS:34157-83-0 |
C29H38O4 |
|
Biological activity and safety of Tripterygium extract prepa...
2012-01-01 [Molecules 17(9) , 11113-23, (2012)] |
|
Inhibitory mechanisms of celastrol on human liver cytochrome...
2015-01-01 [Xenobiotica 45 , 571-7, (2015)] |
|
[Studies on sustained release solid dispersion of tripterine...
2012-10-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 37(20) , 3052-5, (2012)] |
|
Interleukin 34: a new modulator of human and experimental in...
2015-08-01 [Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 129 , 281-90, (2015)] |
|
Celastrol prevents cadmium-induced neuronal cell death via t...
2014-01-01 [J. Neurochem. 128(2) , 256-66, (2014)] |