Porous metal-organic framework with coordinatively unsaturated Mn(II) sites:sorption properties for various gases.
Hoi Ri Moon, Norihito Kobayashi, Myunghyun Paik Suh
Index: Inorg. Chem. 45(21) , 8672-6, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A 3D porous metal-organic framework generating 1D channels, [Mn(NDC)(DEF)]n (1), has been prepared from the solvothermal reaction of Mn(II) and 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid (H2NDC) in diethylformamide (DEF). When DEF molecules coordinating Mn(II), which occupy the channels, are removed from 1 by heating the crystal of 1 at 250 degrees C under vacuum for 18 h, structural change occurs as evidenced by X-ray powder diffraction patterns. Desolvated solid [Mn(NDC)]n (2), which contains coordinatively unsaturated Mn(II) sites, reveals remarkable sorption capabilities for N2, H2, CO2, and CH4 gases and exhibits type I sorption behavior indicative of permanent microporosity.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
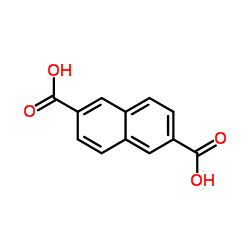 |
2,6-Naphthalenedicarboxylic acid
CAS:1141-38-4 |
C12H8O4 |
|
Decarboxylative polymerization of 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxyli...
2014-07-09 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(27) , 9658-63, (2014)] |
|
Distinct differences in self-assembly of aromatic linear dic...
2009-01-20 [Langmuir 25(2) , 968-72, (2009)] |
|
Measurement of low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids in ambi...
2008-01-01 [Methods Mol. Biol. 384 , 43-64, (2008)] |
|
Analysis of trifluoroacetic acid in lyophilized natural prod...
1997-09-12 [J. Chromatogr. B. Biomed. Sci. Appl. 697(1-2) , 255-7, (1997)] |
|
Interactions of cyclodextrins with aromatic compounds studie...
2002-11-01 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 58(13) , 2983-9, (2002)] |