An anti-cancer derivative of butyric acid (pivalyloxmethyl buterate) and daunorubicin cooperatively prolong survival of mice inoculated with monocytic leukaemia cells.
T Kasukabe, A Rephaeli, Y Honma
Index: Br. J. Cancer 75(6) , 850-4, (1997)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A derivative of butyric acid, pivalyloxymethyl butyrate (AN-9), inhibited the proliferation and induced apoptosis of mouse monocytic leukaemia Mm-A cells, although sodium butyrate, but not AN-9, induced differentiation of the cells. AN-9 and DNA-specific antineoplastic agents synergistically inhibited the growth of Mm-A cells, and the simultaneous treatment was required to evoke the maximum growth-inhibitory effect. On the other hand, there was no synergy between butyrate and the drugs, or AN-9 and anti-metabolic agents in inhibiting the growth of the cells, suggesting that the synergistic effect is specific to AN-9 and DNA-reacting agents. AN-9 as a single agent prolonged the survival of mice inoculated with Mm-A cells in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, administration of AN-9 plus daunorubicin (DNR) markedly prolonged their survival. These results suggest that combination with AN-9 and DNR entails an obvious therapeutic potential.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
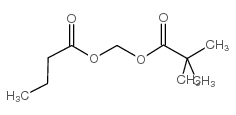 |
AN-9
CAS:122110-53-6 |
C10H18O4 |
|
A phase I study of pivaloyloxymethyl butyrate, a prodrug of ...
2002-07-01 [Clin. Cancer Res. 8(7) , 2142-8, (2002)] |
|
Anticancer derivative of butyric acid (Pivalyloxymethyl buty...
2000-07-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 58(1) , 27-36, (2000)] |
|
Effect of the cytostatic butyric acid pro-drug, pivaloyloxym...
1997-01-01 [J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 123(5) , 267-71, (1997)] |
|
Mitoxantrone mediates demethylation and reexpression of cycl...
2003-01-01 [Cancer Biol. Ther. 2(3) , 259-63, (2003)] |
|
Uptake of pivaloyloxymethyl butyrate into leukemic cells and...
2000-12-01 [J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 126(12) , 693-8, (2000)] |