Avasimibe and atorvastatin synergistically reduce cholesteryl ester content in THP-1 macrophages.
Gemma Llaverías, Mireia Jové, Manuel Vázquez-Carrera, Rosa M Sánchez, Cristina Díaz, Gonzalo Hernández, Juan C Laguna, Marta Alegret
Index: Eur. J. Pharmacol. 451(1) , 11-7, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Evidence suggests that the inhibition of both acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase and hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA reductase causes a synergistic direct antiatherosclerotic effect on the vessel wall. To investigate this synergism in a single cell type and to avoid the confounding effect of plasma cholesterol lowering by these drugs, we have used an in vitro model of human macrophages (phorbol ester-treated THP-1 cells). In macrophages incubated simultaneously with acetyl low-density lipoproteins, the novel acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitor avasimibe (0.01-0.5 microM) caused a concentration-dependent reduction in cell cholesteryl ester content that was not accompanied by an increase in intracellular free cholesterol. A 5 microM concentration of atorvastatin enhanced by approximately twofold the ability of 0.5 microM avasimibe to reduce the mass of esterified cholesterol, and this was reversed by co-incubation with 200 microM mevalonate or 10 microM geranyl-geraniol. Based on these data, we propose that the synergism between acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase and hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors found in several in vivo studies may be explained by a direct additive effect of both agents reducing the lipid content of the macrophages present in the lesion area.Copyright 2002 Elsevier Science B.V.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
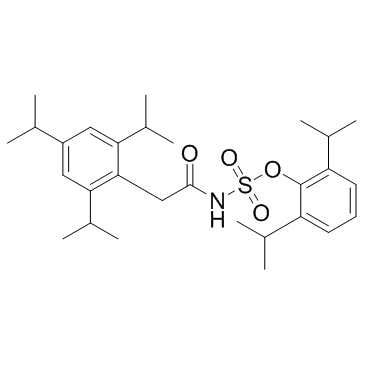 |
Avasimibe
CAS:166518-60-1 |
C29H43NO4S |
|
Statin therapy alone and in combination with an acyl-CoA:cho...
2007-01-01 [Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 36(1) , 9-17, (2007)] |
|
Coronary circulatory function in patients with the metabolic...
2011-09-01 [J. Nucl. Med. 52(9) , 1369-77, (2011)] |
|
Anti-atherogenic effects of the acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltra...
2002-03-01 [Atherosclerosis 161(1) , 45-54, (2002)] |
|
Effects of avasimibe on cytochrome P450 2C9 expression in vi...
2004-12-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 32(12) , 1370-6, (2004)] |
|
New advances in lipid-modifying therapies for reducing cardi...
2002-01-01 [Cardiology 97(2) , 59-66, (2002)] |