Inhibitory effect of cytochalasin H on cell reaggregation of the fresh water sponge, Ephydatia meyeni Carter.
S Ghaskadbi, L Mulherkar
Index: Exp. Cell Biol. 50(3) , 155-61, (1982)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Cytochalasin H (CH) has been shown to inhibit the reaggregation of dissociated cells of a fresh water sponge. The effect is dose-dependent and reversible. Even after 24 h of CH treatment, the cells show the formation of pseudopodia suggesting that the effect of CH may not be due to arrested cell motility. Exogenously added alpha-D-glucosamine, a precursor of complex carbohydrates, brings about reaggregation of CH-treated cells. Fluorescent Con A binding, both patching and capping, is shown by untreated as well as CH-treated cells. It is likely that CH, like cytochalasin B, may interfere with the production, release or binding of carbohydrate-containing macromolecules important in cell aggregation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
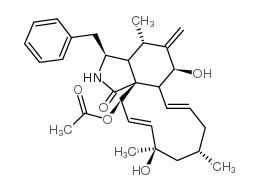 |
Cytochalasin H
CAS:53760-19-3 |
C30H39NO5 |
|
A new fungal isolate from Paspalum scrobiculatum, Linn. with...
1975-01-01 [Acta Microbiol. Acad. Sci. Hung. 22 , 253, (1975)] |
|
Effects of cytochalasin H on chick embryo explants cultured ...
1984-12-01 [Toxicology 33(3-4) , 323-30, (1984)] |
|
L-696,474, a novel cytochalasin as an inhibitor of HIV-1 pro...
1992-05-01 [J. Antibiot. 45(5) , 679-85, (1992)] |
|
Characterization of kinase suppressor of Ras-1 expression an...
2009-04-01 [Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 63(5) , 807-18, (2009)] |
|
Stimulation of Respiratory Motor Output and Ventilation in a...
2015-09-01 [Platelets 11(8) , 467-76, (2000)] |