Effects of ethylene glycol-based graft, star-shaped, and dendritic polymers on solubilization and controlled release of paclitaxel.
Tooru Ooya, Jaehwi Lee, Kinam Park
Index: J. Control. Release 93(2) , 121-7, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
New methods and pharmaceutical compositions were developed to increase the aqueous solubility of paclitaxel (PTX), a poorly water-soluble drug. Graft and star-shaped graft polymers consisting of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG400) graft chains increased the PTX solubility in water by three orders of magnitude. Polyglycerol dendrimers (dendriPGs) dissolved in water at high concentrations without significantly increasing the viscosity and, at 80 wt.%, were found to increase the solubility of PTX 10,000-fold. The solubilized PTX was released from graft polymers, star-shaped graft polymers, and the dendriPGs into the surrounding aqueous solution. The release rate was a function of the star shape and the dendrimer generation. The availability of the new graft, star and dendritic polymers having ethylene glycol units should permit development of novel delivery systems for other poorly water-soluble drugs.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
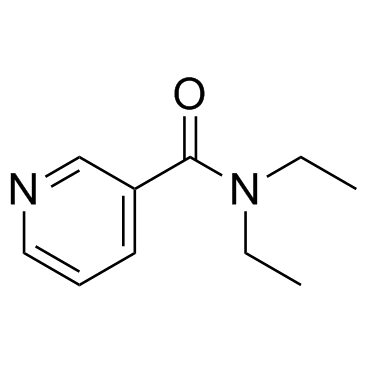 |
Nikethamide
CAS:59-26-7 |
C10H14N2O |
|
High throughput quantification of prohibited substances in p...
2014-12-29 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1374 , 40-9, (2014)] |
|
Screening method for stimulants in urine by UHPLC-MS/MS: ide...
2015-09-01 [Drug Test. Anal. 7 , 819-30, (2015)] |
|
Mechanistic studies on hydrotropic solubilization of nifedip...
1998-01-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 46(1) , 125-30, (1998)] |
|
[Disturbed functioning of enzyme systems of microsomal oxida...
2000-03-01 [Biull. Eksp. Biol. Med. 129(3) , 297-301, (2000)] |
|
[Disturbed functioning of enzyme systems of the microsomal o...
2000-01-01 [Biull. Eksp. Biol. Med. 129(1) , 56-60, (2000)] |