Determination of phytic acid and inositolphosphates in barley.
František Kvasnička, Jana Copíková, Rudolf Sevčík, Eliška Václavíková, Andriy Synytsya, Kateřina Vaculová, Michal Voldřich
Index: Electrophoresis 32 , 1090-1093, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Phytic acid (PA) and lower inositolphosphates (InsP(n) ) is the main storage form of phosphorus in grains or seeds. The content of PA and InsP(n) in different varieties of barley was analyzed by capillary isotachophoresis and online-coupled capillary isotachophoresis with CZE. The electrolytes (in demineralized water) for the isotachophoretic analysis consisted of 10 mM HCl, 14 mM glycylglycine, and 0.1% 2-hydroxyethylcellulose (leading) and 10 mM citric acid (terminating). The optimized electrolytes for the online coupling isotachophoresis with zone electrophoresis analysis were mixtures of 5 mM HCl, 7 mM glycylglycine, and 0.1% 2-hydroxyethylcellulose (leading), 20 mM citric acid, 10 mM glycylglycine, and 0.1% 2-hydroxyethylcellulose (background) and 10 mM citric acid (terminating). PA and all studied InsP(n) were separated within 25 min and detected by a conductivity detector. Simple sample preparation (acidic extraction), sufficient sensitivity, speed of analysis, and low running cost are important attributes of the electrophoretic methods. The method was used for the determination of PA and InsP(n) in barley varieties within an ongoing research project.Copyright © 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
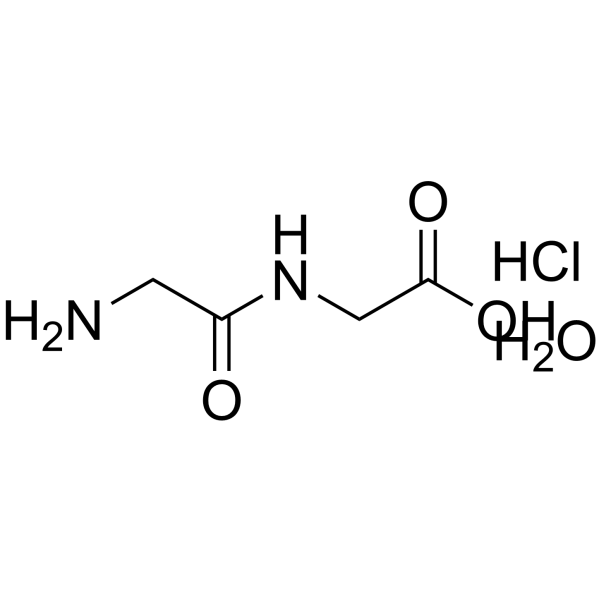 |
Gly-GLY.HCl.H2O
CAS:23273-91-8 |
C4H11ClN2O4 |
|
Native and fluorescent dye-dependent single-DNA molecule mic...
2011-08-28 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 47 , 9137-9139, (2011)] |
|
Hydrated metal(II) complexes of N-(6-amino-3,4-dihydro-3-met...
2004-02-01 [Acta Crystallogr. B 60 , 46-64, (2004)] |
|
In Situ Porous Structures: A Unique Polymer Erosion Mechanis...
2011-07-01 [Adv. Funct. Mater. 20 , 2743-2757, (2010)] |
|
Improved rapid assay of plasma uric acid by short-end inject...
2009-12-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 395 , 2577-2582, (2009)] |
|
Sodium glycylglycine as effective electrolyte run buffer for...
2005-11-01 [J. Sep. Sci. 28 , 2193-2199, (2005)] |