Phosphorylation of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose by D-xylulokinase of Escherichia coli.
J Wungsintaweekul, S Herz, S Hecht, W Eisenreich, R Feicht, F Rohdich, A Bacher, M H Zenk
Index: Eur. J. Biochem. 268(2) , 310-6, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of the vitamins thiamine and pyridoxal and for the formation of isopentenyl pyrophosphate and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate via the nonmevalonate pathway of terpenoid biosynthesis. Earlier studies had shown that Escherichia coli incorporates unphosphorylated 1-deoxy-D-xylulose into the terpenoid side chain of ubiquinones with high efficacy. We show that D-xylulokinase of E. coli (EC 2.7.1.17) catalyzes the phosphorylation of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose at the hydroxy group of C-5 at a rate of 1.6 micromol.mg min-1. This reaction constitutes a potential salvage pathway for the generation of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate from exogenous or endogenous 1-deoxy-D-xylulose as starting material for the biosynthesis of terpenoids, thiamine and pyridoxal.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
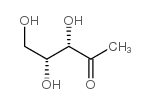 |
1-Deoxy-D-xylulose
CAS:60299-43-6 |
C5H10O4 |
|
Systems analysis of methylerythritol-phosphate pathway flux ...
2015-01-01 [Microb. Cell Fact. 14(1) , 193, (2015)] |
|
Biosynthesis of 2-methyl-3-buten-2-ol emitted from needles o...
2001-06-01 [Planta 213(2) , 323-6, (2001)] |
|
Genetic evidence for the role of isopentenyl diphosphate iso...
2008-04-01 [Plant Cell Physiol. 49(4) , 604-16, (2008)] |
|
Biosynthesis of mono- and sesquiterpenes in strawberry fruit...
2006-02-22 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 54(4) , 1473-8, (2006)] |
|
Cloning and characterization of the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol ...
2008-11-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 72(11) , 2903-17, (2008)] |