The coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate inhibits the self-splicing of the group I intron.
Sung Joon Ahn, In Kook Park
Index: Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 35(2) , 157-67, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Effects of the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate and its analogs on the inhibition of self-splicing of primary transcripts of the phage T4 thymidylate synthase gene (td) were investigated. Of all compounds tested, the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate was the most potent inhibitor and the order of inhibitory efficiency for compounds tested was as follows: thiamine pyrophosphate>thiamine monophosphate>thiamine>thiochrome. Increasing guanosine concentration overcame the suppression of self-splicing by thiamine pyrophosphate close to the level of normal splicing. Kinetic analysis demonstrated that thiamine pyrophosphate acts as a competitive inhibitor for the td intron RNA with a Ki of 2.2mM. The splicing specificity inhibition by thiamine pyrophosphate is predominantly due to changes in Km.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
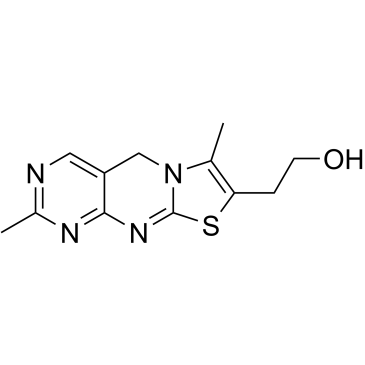 |
Thiochrome
CAS:92-35-3 |
C12H14N4OS |
|
Functional activation of G-proteins coupled with muscarinic ...
2014-01-01 [J. Pharmacol. Sci. 125(2) , 157-68, (2014)] |
|
Salvage of the thiamin pyrimidine moiety by plant TenA prote...
2014-10-01 [Biochem. J. 463(1) , 145-55, (2014)] |
|
Determination of thiamine and its phosphate esters in rat ti...
2005-02-25 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 816(1-2) , 67-72, (2005)] |
|
Thiamine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli: in vitro reconsti...
2004-04-23 [J. Biol. Chem. 279(17) , 17054-62, (2004)] |
|
A reliable semiautomated method for the determination of tot...
1982-01-01 [Ann. Clin. Biochem. 19(Pt 1) , 52-6, (1982)] |