Antimicrobial properties of 2 aliphatic amines and chlorhexidine in vitro and in saliva.
A M Salem, D Adams, H N Newman, L W Rawle
Index: J. Clin. Periodontol. 14(1) , 44-7, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The surfactants tetradecylamine, hexadecylamine and chlorhexidine have been compared with regard to their ability to inhibit microbial growth. Antibacterial activity was assessed by tube dilution methods. Tetradecylamine and chlorhexidine were similar in antibacterial activity, being effective at low concentrations against most organisms tested. Hexadecylamine also inhibited growth but at higher concentrations. Viable counts of salivary organisms were monitored in volunteers over 48 h after one rinse with the agents. The initial reduction in numbers of total viable salivary bacteria and streptococci by tetradecylamine and of streptococci by hexadecylamine had disappeared 3 h after a single mouth rinse, but the reduction in numbers of all salivary bacteria by chlorhexidine was more prolonged.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
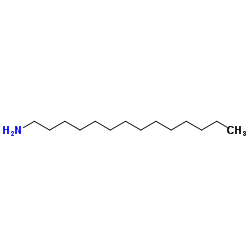 |
1-Tetradecanamine
CAS:2016-42-4 |
C14H31N |
|
Controlling the size of hot injection made nanocrystals by m...
2015-02-25 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137(7) , 2495-505, (2015)] |
|
Accurate assessment of the biodegradation of cationic surfac...
2015-08-01 [Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 118 , 83-9, (2015)] |
|
Temperature- and pH-Dependent Shattering: Insoluble Fatty Am...
2015-09-01 [Langmuir 31 , 9312-24, (2015)] |
|
Inhibition by alkylamines of NADPH oxidase through blocking ...
1999-07-01 [Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 80(3) , 237-42, (1999)] |
|
[Chromatographic properties of tetradecylamine bonded statio...
1999-07-01 [Se Pu 17(4) , 339-41, (1999)] |