| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
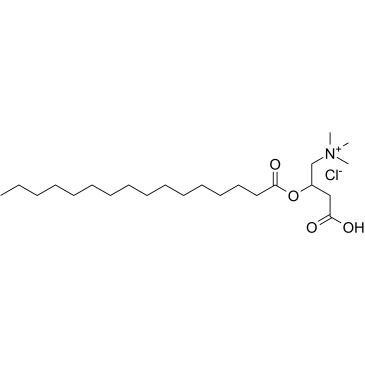 |
UNII:EIL57224QR
CAS:6865-14-1 |
|
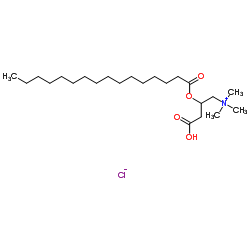 |
L-Palmitoylcarnitine chloride
CAS:18877-64-0 |