Physical properties of [Formula: see text] polymer electrolytes: nuclear magnetic resonance investigation and comparison with [Formula: see text].
C Roux, W Gorecki, J Y Sanchez, M Jeannin, E Belorizky
Index: J. Phys. Condens. Matter 8 , 7005, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The physical properties of the ionic conductor [Formula: see text], obtained by dissolution of lithium trifluoromethanesulphonylimide in poly(propylene oxide), have been investigated for several values of n. The glass transition temperature [Formula: see text] has been established from both DSC and NMR techniques. The diffusion coefficients of [Formula: see text]-containing species have been determined by the pulsed magnetic field gradient technique. The behaviour of the proton relaxation time [Formula: see text] versus temperature and concentration has been correlated to the glass temperature. The behaviour of the proton transverse relaxation function, obtained by the spin-echo technique, has been interpreted using a simple model in which two regimes and consequently two transverse relaxation times coexist and are assigned to the `entangled' and `non-entangled' parts of the high-molecular-weight polymer chains investigated.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
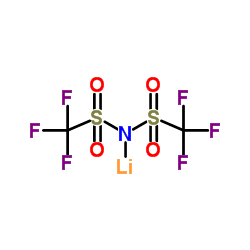 |
Lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulphonyl)imide
CAS:90076-65-6 |
C2F6LiNO4S2 |
|
Nanoporous Cathodes for High-Energy Li-S Batteries from Gyro...
2015-06-23 [ACS Nano 9 , 6147-57, (2015)] |
|
Preparation and evaluation of surface-bonded tricationic ion...
2015-05-29 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1396 , 62-71, (2015)] |
|
Development of bipolar all-solid-state lithium battery based...
2015-01-01 [Sci. Rep. 5 , 8869, (2015)] |
|
Development and characterization of poly(1-vinylpyrrolidone-...
2014-01-01 [ScientificWorldJournal 2014 , 254215, (2014)] |
|
Effect of ion distribution on conductivity of block copolyme...
2009-03-01 [Nano Lett. 9(3) , 1212-6, (2009)] |