The application of 19F nuclear magnetic resonance to investigate microbial biotransformations of organofluorine compounds.
Cormac D Murphy
Index: OMICS 11(3) , 314-24, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Fluorinated organic compounds, although rare in nature, are significant environmental contaminants owing to the numerous applications for which this class of compounds is employed. It is important that biodegradation of these compounds can be readily assessed in order to provide information on their fate in the environment. Fluorine-19 nuclear magnetic resonance (19F NMR) spectroscopy has emerged as a very useful technique to readily determine the catabolism of fluorinated aromatic compounds by microorganisms, either in whole cell or cell-free systems. The principal advantage of this technique is that fluorinated compounds can be observed directly in the culture supernatant or enzyme assay, without purification or derivatization. In this review an account of the application of 19F NMR in the study of microbial metabolism of organofluorine compounds is presented.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
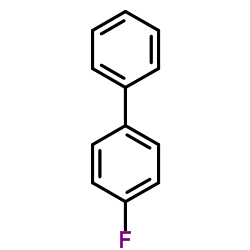 |
4-Fluorobiphenyl
CAS:324-74-3 |
C12H9F |
|
Update on biological actions of 1alpha,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 (r...
2002-11-29 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 31(10) , 1849-56, (1982)] |
|
Metabolism of 4-fluoroaniline and 4-fluorobiphenyl in the ea...
2002-06-01 [Xenobiotica 32(6) , 479-90, (2002)] |
|
Biotransformation of fluorobiphenyl by Cunninghamella elegan...
2010-03-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 86(1) , 345-51, (2010)] |
|
Anaerobic degradation of the aromatic hydrocarbon biphenyl b...
2009-04-01 [FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 68(1) , 86-93, (2009)] |
|
Degradation of 4-fluorobiphenyl in soil investigated by 19F ...
1999-02-01 [Chemosphere 38(5) , 1085-101, (1999)] |