| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
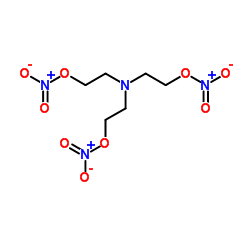 |
Bentonite
CAS:1302-78-9 |
|
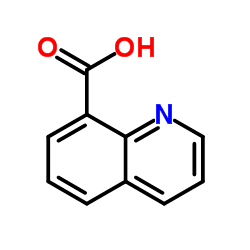 |
Quinoline-8-carboxylic acid
CAS:86-59-9 |