Microbial growth on 2-bromobutane.
G T Sperl, J McKae
Index: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 46(4) , 331-41, (1980)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A member of the genus Arthrobacter was isolated which grew at the expense of 2-bromobutane as sole source of carbon and energy. Evidence is presented which suggests that the initial conversion of 2-bromobutane to 2-butanol is a spontaneous chemical hydrolysis and not mediated by the organism. Further evidence from oxygen consumption experiments indicates that 2-bromobutane is oxidized through 2-butanol, methyl ethyl ketone, ethyl acetate to acetate and ethanol. Results of experiments with cells grown on pathway intermediates reveal that the enzymes necessary for the oxidation of 2-butanol, methyl ethyl ketone, ethyl acetate, ethanol and acetaldehyde are not coordinately, but individually induced by their respective substrates.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
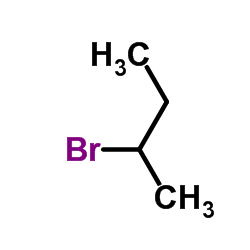 |
2-Bromobutane
CAS:78-76-2 |
C4H9Br |
|
Validated methods for degrading hazardous chemicals: some ha...
1991-06-01 [Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 52(6) , 252-7, (1991)] |
|
Enantioselective surface chemistry of R-2-bromobutane on Cu(...
2006-06-01 [J. Phys. Chem. B 110(21) , 10411-20, (2006)] |
|
Selective Reactivity in Gas-Liqiud Chromatography. Determina...
[Anal. Chem. 31(1) , 114-7, (1959)] |
|
STEREOCHEMISTRY AND ISOTOPE EFFECT IN THE DEHYDROBROMINATION...
[Chem. Lett. 1(7) , 551-2, (1972)] |
|
Viscosities of binary mixtures of 2-bromobutane and 2-bromo-...
[Int. J. Thermophys. 23(6) , 1455-1468, (2002)] |