Tuning the adhesion of silica microparticles to a poly(2-vinyl pyridine) brush: an AFM force measurement study.
Astrid Drechsler, Alla Synytska, Petra Uhlmann, Manfred Stamm, Friedrich Kremer
Index: Langmuir 28(44) , 15555-65, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
AFM force measurements have been performed to study the influence of the pH value and salt concentration on the interactions between poly(2-vinyl pyridine) brushes and microsized silica spheres, focusing on attractive and adhesion forces. It was found that the interaction was composed of a repulsive component reflecting the conformation of the brush and an additional attractive force. It can therefore be switched reversibly between purely repulsive at pH 2.5 to strong and medium adhesion by changing the pH value to pH 4 and 6, respectively. Addition of KCl showed different effects: at pH 2.5 high salt concentrations induced an attractive force; at pH 4 the interaction changed from strong attraction in the osmotic brush regime to repulsion and weaker adhesion in the salted brush regime; at pH 6 increase of the KCl concentration weakened the attractive force. These effects could partly be explained by the theory of polyelectrolyte brushes; under some conditions the mechanism of the attractive force is still unclear.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
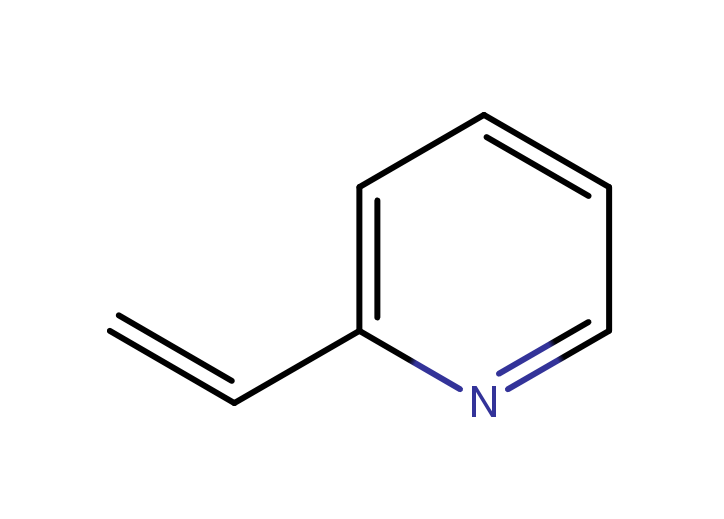 |
poly(2-vinylpyridine)
CAS:25014-15-7 |
C7H7N |
|
Core-crosslinked compartmentalized cylinders.
2011-01-01 [Nanoscale 3(1) , 288-97, (2011)] |
|
Fluorescent nanoparticles stabilized by poly(ethylene glycol...
2010-07-06 [Langmuir 26(13) , 10684-92, (2010)] |
|
Adsorption of 5-sodiosulfoisophthalic acids from aqueous sol...
2010-03-15 [J. Hazard. Mater. 175(1-3) , 111-6, (2010)] |
|
In situ metallization of patterned polymer brushes created b...
2013-04-19 [Nanotechnology 24(15) , 155602, (2013)] |
|
Gold nanoparticles grown on star-shaped block copolymer mono...
2011-09-06 [Langmuir 27(17) , 10730-8, (2011)] |