Evidence for a radical mechanism of the dechlorination of chlorinated propenes mediated by the tetrachloroethene reductive dehalogenase of Sulfurospirillum muftivorans.
Roland P H Schmitz, Julia Wolf, Andreas Habel, Anke Neumann, Kerstin Ploss, Ales Svatos, Wilhelm Boland, Gabriele Diekert
Index: Environ. Sci. Technol. 41(21) , 7370-5, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated propenes was studied with the tetrachloroethene reductive dehalogenase purified from Sulfurospirillum multivorans to obtain indications for a radical mechanism of this reaction. When reduced methyl viologen (MV), which is a radical cation, was applied as electron donor for the reduction of different chloropropenes, a significant part of MV could not be rereduced with Ti(III) citrate, indicating that a part of the MV was consumed in a side reaction. Mass spectrometric analysis of assays with MV as electron donor revealed the formation of side products, the masses of which might account for the formation of adducts from a chloropropenyl radical and reduced methyl viologen. With Ti(III) citrate as sole electron donor, 2,3-dichloropropene was reduced and as a side product, 2,5-dichloro-1,5-hexadiene was formed demonstrating that the reductive dechlorination of 2,3-dichloropropene proceeds via a radical reaction mechanism. The results support different dehalogenation mechanisms forthe reductive dechlorination of chloropropenes and halogenated ethenes.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
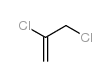 |
2,3-Dichloropropene
CAS:78-88-6 |
C3H4Cl2 |
|
Halogenated derivatives QSAR model using spectral moments to...
2008-05-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 5720-32, (2008)] |
|
Mutagenicity of chloroolefins in the Salmonella/mammalian mi...
1986-01-01 [Mutat. Res. 170(1-2) , 1-9, (1986)] |
|
Effect of vapor concentration on the disposition of inhaled ...
1985-10-01 [Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 5(5) , 997-1005, (1985)] |
|
Metabolism of 2,3-dichloro-1-propene in the rat. Considerati...
1988-01-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 16(1) , 60-8, (1988)] |
|
Disposition of [14C]2,3-dichloropropene in Fischer-344 rats ...
1984-10-01 [Toxicol. Lett. 23(1) , 119-25, (1984)] |