Functional expression of the peptide transporter PEPT2 in the mammalian enteric nervous system.
Anne Rühl, Susanne Hoppe, Isabelle Frey, Hannelore Daniel, Michael Schemann
Index: J. Comp. Neurol. 490(1) , 1-11, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The peptide transporter PEPT2 mediates transmembrane uptake of small peptides. So far, its expression has not been evidenced in the gastrointestinal tract. We have investigated peptide transport activity in the neuromuscular layers of the gastrointestinal tract by using the fluorescent tracer-dipeptide beta-Ala-Lys-Nepsilon-7-amino-4-methyl-coumarin-3-acetic acid (Ala-Lys-AMCA). Whole-mount preparations from mouse, rat, and guinea pig stomach and small and large intestine were incubated with Ala-Lys-AMCA in the presence or absence of the uptake-inhibitors L-histidine, D-phenylalanyl-L-alanine (D-Phe-Ala), glycyl-L-sarcosine (Gly-Sar), glycyl-L-glutamine (Gly-Gln), benzylpenicillin, and cefadroxil. Fluorescence microscopy revealed that Ala-Lys-AMCA specifically accumulated in both ganglionic layers of the enteric nervous system (ENS) in all regions and species studied. This could be inhibited by Gly-Sar, D-Phe-Ala, Gly-Gln, and cefadroxil, but not by free histidine and benzylpenicillin, indicating uptake via PEPT2. Accordingly, dipeptide uptake was completely abolished in PEPT2-deficient mice. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis detected a PEPT2-specific transcript in extracts from the ganglionic ENS layers of mouse small and large intestine, further proving that enteric dipeptide transport activity is specifically mediated via PEPT2. The cellular site of dipeptide uptake was immunohistochemically localized to enteric glial cells and tissue-resident macrophages. In addition, dipeptide uptake occurred in a neurochemically defined subset of neurons in the guinea pig ENS. Our results constitute the first functional evidence for dipeptide transport activity in the ENS. PEPT2-mediated dipeptide transport in enteric glia could contribute to the clearance of neuropeptides in the ENS. In addition, the fluorophore-coupled dipeptide uptake via PEPT2 is a novel vital marker for glial cells in the ENS.Copyright (c) 2005 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
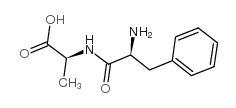 |
Phe-Ala
CAS:3918-87-4 |
C12H16N2O3 |
|
Alkali metal complexes of the dipeptides PheAla and AlaPhe: ...
2008-03-14 [ChemPhysChem 9 , 579-589, (2008)] |
|
Single-conformation ultraviolet and infrared spectroscopy of...
2008-04-09 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(14) , 4795-807, (2008)] |
|
A novel inhibitor of the mammalian peptide transporter PEPT1...
2001-04-10 [Biochemistry 40(14) , 4454-8, (2001)] |
|
P3 cap modified Phe*-Ala series BACE inhibitors.
2004-01-05 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14(1) , 245-50, (2004)] |
|
Dipeptide transport characteristics of the apical membrane o...
1995-08-01 [Am. J. Physiol. 269(2 Pt 1) , L137-43, (1995)] |