| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
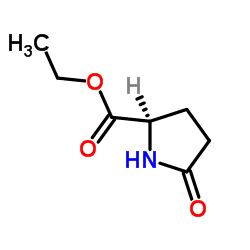 |
H-D-Pyr-OEt
CAS:68766-96-1 |
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
H-D-Pyr-OEt
CAS:68766-96-1 |