| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
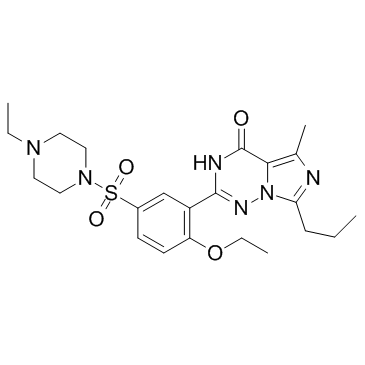 |
Vardenafil
CAS:224785-90-4 |
|
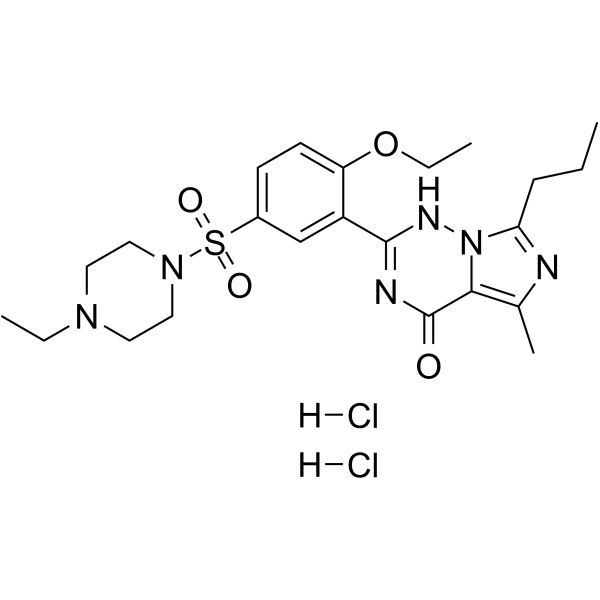 |
Vardenafil dihydrochloride
CAS:224789-15-5 |