Thiolutin inhibits utilization of glucose and other carbon sources in cells of Escherichia coli.
R Bergmann
Index: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 55(2) , 143-52, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Thiolutin was found to inhibit the utilization of glucose and other growth substrates in Escherichia coli. The inhibition was detected by a sharp drop of the respiration rate after addition of the antibiotic. The actual function affected was allocated to the cytoplasmic membrane of the bacterial cells by the following evidence: --spheroplasts were affected like intact cells, --individual reactions of either the electron transport chain or the glycolytic pathway were not inhibited, --glucose consumption in the culture stopped and the cells accumulated guanosine tetraphosphate as under starvation conditions, --activation of the cell's apo-glucose dehydrogenase restored respiration via bypassing the glucose phosphotransferase system. It was concluded that the transport of certain substrates across the membrane was inhibited.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
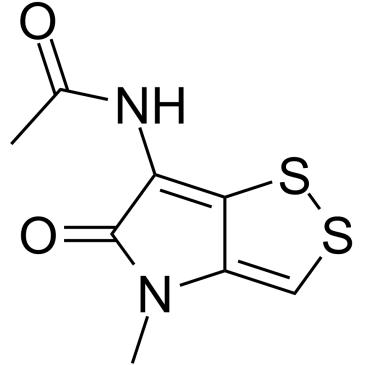 |
Thiolutin
CAS:87-11-6 |
C8H8N2O2S2 |
|
Condensin targets and reduces unwound DNA structures associa...
2015-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 6 , 7815, (2015)] |
|
Thiophene-degrading Escherichia coli mutants possess sulfone...
1990-10-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56(10) , 3179-85, (1990)] |
|
Mapping of two transcription mutations (tlnI and tlnII) conf...
1980-01-01 [Mol. Gen. Genet. 180(3) , 609-15, (1980)] |
|
The transcriptional inhibitor thiolutin blocks mRNA degradat...
2008-02-01 [Yeast 25(2) , 85-92, (2008)] |
|
Thiolutin-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium.
1982-10-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 22(4) , 541-7, (1982)] |