Toxicological European research. Recherche europeenne en toxicologie
1981-11-01
[Hepatic microsomal monoxygenase inhibition by nabam in the rat (author's transl)].
A Périquet, R Derache
Index: Toxicol. Eur. Res. 3(6) , 285-91, (1981)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Nabam (fungicide dithiocarbamate) has been incorporated with the diet of rats during six months (the doses were: 0, 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000 and 2000 ppm). It decreases significantly the hepatic microsomal enzymes activity (aniline hydroxylase and aminopyrine N-demethylase and the liver P 450 content, but the cytochrome b 5 concentration doesn't seem to be modified. The microsomal lipidic and proteic content is only modified with the highest Nabam dose. Several hypotheses may be proposed to explain the Nabam effects: one is the inhibition of the monooxygenases and their biosynthesis repression.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
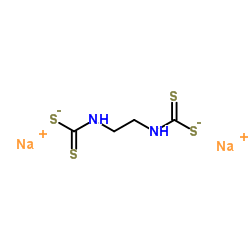 |
Nabam
CAS:142-59-6 |
C4H6N2Na2S4 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Ultrastructural and histological study of degenerative chang...
1983-05-01 [J. Invertebr. Pathol. 41(3) , 281-300, (1983)] |
|
Studies on the mechanism of nabam- and zineb-induced inhibit...
1985-12-01 [Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 81(3 Pt 1) , 460-8, (1985)] |
|
[Effects of the fungicides, nabam and zineb, on oxygenase ac...
1981-12-01 [Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 19(6) , 761-3, (1981)] |
|
Determination of nabam fungicide in crops by liquid chromato...
1991-01-01 [J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 74(2) , 384-8, (1991)] |
|
Photodegradation and flow-injection determination of dithioc...
2009-03-01 [Anal. Sci. 25(3) , 395-400, (2009)] |