The effect of repeated exposure to azamethiphos on survival and spawning in the American lobster (Homarus americanus).
L E Burridge, K Haya, S L Waddy
Index: Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 69(3) , 411-5, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The azamethiphos formulation Salmosan has been used to control sea lice on Atlantic salmon. To determine the effect of this pesticide on spawning in the American lobster, pre-ovigerous females acclimated to 13 degrees C were given biweekly 1-h exposures to Salmosan at concentrations of 1.25-10 microg/L azamethiphos. In March and April, four exposures to 1.25, 2.5, or 5.0 microg/L had no significant effect on survival or spawning incidence, while three or four exposures to 10 microg/L caused high mortality (43-100%). Spawning incidence in the surviving lobsters in the 10 microg/L groups was significantly reduced in the group given four treatments, but not in the group given three treatments. In December and January, four exposures to 10 microg/L azamethiphos had no significant effect on either survival or spawning incidence. The results demonstrate that repeated 1-h biweekly exposures to azamethiphos can have a negative effect on survival and spawning in female American lobsters. The response to this pesticide appears to be influenced by time of year, as well as concentration and number of exposures.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
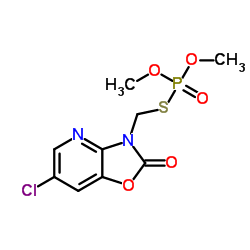 |
Azamethiphos
CAS:35575-96-3 |
C9H10ClN2O5PS |
|
Albumin binding as a potential biomarker of exposure to mode...
2008-06-01 [Biol. Cell 13 , 343-63, (2008)] |
|
Evaluation of insecticidal efficiency of certain new selecti...
1992-12-01 [J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 22(3) , 839-49, (1992)] |
|
Characterisation of esterases as potential biomarkers of pes...
2008-03-01 [Environ. Pollut. 152(2) , 342-50, (2008)] |
|
Effect of synergists on the oral and topical toxicity of aza...
1992-08-01 [J. Econ. Entomol. 85(4) , 1041-5, (1992)] |
|
The lethality of Salmosan (Azamethiphos) to American lobster...
1999-06-01 [Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 43(2) , 165-9, (1999)] |