| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
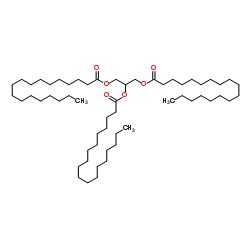 |
Tristealin
CAS:555-43-1 |
|
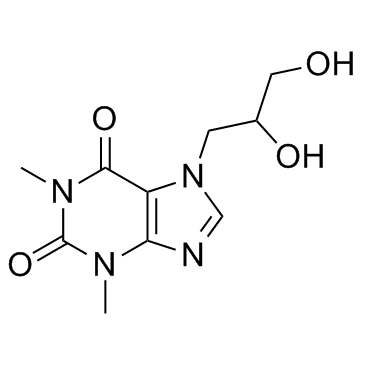 |
Diprophylline
CAS:479-18-5 |