| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
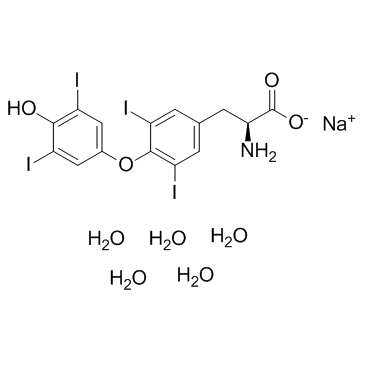 |
Sodium levothyroxine pentahydrate
CAS:6106-07-6 |
|
 |
1,1,4,4-TETRAPHENYL-1,3-BUTADIENE
CAS:1450-63-1 |