Role of pencycuron in aflatoxin production and cotton seed protection.
H A Hasan
Index: J. Nat. Toxins 10(2) , 127-36, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The research is conducted on the effect of pencycuron and pencycuron-c on cotton seed mycoflora, aflatoxin production and viability. At 8% seed moisture content (mc), pencycuron and pencycuron-c promoted Aspergillus niger, A. flavus, and Penicillium corylophilum growth count at 1 g/kg, but exerted inhibitory effect at 3 and 5 g/kg. At 15% mc, pencycuron enhanced seed-borne fungi at all three doses after most treatment periods (1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 months), whereas pencycuron-c induced inhibition effect. The A. niger utilized pencycuron as nitrogen source more than pencycuron-c. Seeds with 15% mc lost their viability faster than that at 8%, and this was more evident as storage time increased. Such loss occurred faster when seed was treated with pencycuron, whereas pencycuron-c exerted significant activation in the viability compared to the control. The fungal species have high biodegradation activity and produce aflatoxin in different parts of cotton boll (fiber, valves, and seeds). Pencycuron and pencycuron-c inhibited aflatoxin B1 and B2 production in seeds, but did not affect aflatoxin G1 and G2.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
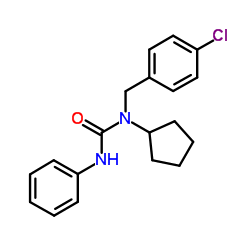 |
Pencycuron
CAS:66063-05-6 |
C19H21ClN2O |
|
Interactions between nematophagous fungi and consequences fo...
2003-01-01 [Mycol. Res. 107(Pt 1) , 47-56, (2003)] |
|
Detection of iprobenfos and edifenphos using a new multi-apt...
2015-04-08 [Anal. Chim. Acta 868 , 60-6, (2015)] |
|
Effect of carbendazim and pencycuron on soil bacterial commu...
2009-12-15 [J. Hazard. Mater. 172(1) , 84-91, (2009)] |
|
Dissipation of pencycuron in rice plant.
2005-08-01 [J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 6(8) , 756-8, (2005)] |
|
Use of ion cluster analysis in a metabolic study of pencycur...
1982-01-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 30(6) , 1061-7, (1982)] |