Increasing the levels of 2-phenylethyl acetate in wine through the use of a mixed culture of Hanseniaspora osmophila and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Fernando Viana, José V Gil, Salvador Vallés, Paloma Manzanares
Index: Int. J. Food Microbiol. 135(1) , 68-74, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The impact of mixed cultures of Hanseniaspora osmophila and Saccharomyces cerevisiae with different initial yeast ratios on wine composition has been examined. The mixed culture significantly affected sugar consumption, the main enological parameters and ester concentrations, with the exception of glycerol, isoamyl acetate and diethyl succinate levels. Remarkably, in wines obtained with mixed cultures the concentration of 2-phenylethyl acetate was approximately 3- to 9-fold greater than that produced by S. cerevisiae pure culture. Moreover sensory evaluation revealed a stronger fruity character in wines fermented with mixed cultures than in control wines. Independently of the mixed culture used, all wines showed concentrations of acetic acid and ethyl acetate within the ranges described for wines. Our data suggest that a mixed culture of H. osmophila and S. cerevisiae can be used as a tool to increase 2-phenylethyl acetate in wine and that its concentration can be controlled by modulating the initial yeast ratio in the culture.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
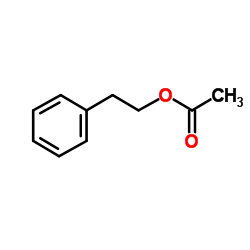 |
Phenethyl acetate
CAS:103-45-7 |
C10H12O2 |
|
Combined effects of nutrients and temperature on the product...
2015-03-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99(5) , 2291-304, (2015)] |
|
Comparative metabolic profiling to investigate the contribut...
2012-03-01 [J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39(3) , 477-94, (2012)] |
|
Impact of addition of aromatic amino acids on non-volatile a...
2014-01-17 [Int. J. Food Microbiol. 170 , 12-20, (2014)] |
|
Adaptive evolution of the lager brewing yeast Saccharomyces ...
2013-05-01 [FEMS Yeast Res. 13(3) , 335-49, (2013)] |
|
Fragrance material review on phenethyl acetate.
2012-09-01 [Food Chem. Toxicol. 50 Suppl 2 , S491-7, (2012)] |