Enzymatic synthesis of puerarin glucosides using Leuconostoc dextransucrase.
Jin-A Ko, Young Bae Ryu, Tae-Soon Park, Hyung Jae Jeong, Jang-Hoon Kim, Su-Jin Park, Joong-Su Kim, Doman Kim, Young-Min Kim, Woo Song Lee
Index: J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 22(9) , 1224-9, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Puerarin (P), an isoflavone derived from kudzu roots, has strong biological activities, but its bioavailability is often limited by its low water solubility. To increase its solubility, P was glucosylated by three dextransucrases from Leuconostoc or Streptococcus species. Leuconostoc lactis EG001 dextransucrase exhibited the highest productivity of puerarin glucosides (P-Gs) among the three tested enzymes, and it primarily produced two P-Gs with a 53% yield. Their structures were identified as alpha-D-glucosyl-(1-->6)-P (P-G) by using LC-MS or (1)H- or (13)C-NMR spectroscopies and alpha-D-isomaltosyl-(1-->6)-P (P-IG2) by using specific enzymatic hydrolysis, and their solubilities were 15- and 202-fold higher than that of P, respectively. P-G and P-IG2 are easily applicable in the food and pharmaceutical industries as alternative functional materials.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
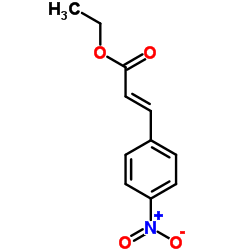 |
Dextran sucrase
CAS:9032-14-8 |
C11H11NO4 |
|
Branching pattern of gluco-oligosaccharides and 1.5kDa dextr...
2013-04-15 [Carbohydr. Polym. 94(1) , 567-76, (2013)] |
|
Purification, optimization of assay, and stability studies o...
2013-01-01 [Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 43(4) , 329-41, (2013)] |
|
Synthesis and characterization of ampelopsin glucosides usin...
2012-12-10 [Enzyme Microb. Technol. 51(6-7) , 311-8, (2012)] |
|
Inhibition of dextransucrase activity in Streptococcus mutan...
2013-02-01 [Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 50(1) , 48-53, (2013)] |
|
Enzymatic synthesis of alkyl glucosides using Leuconostoc me...
2009-09-01 [Biotechnol. Lett. 31(9) , 1433-8, (2009)] |