Endothelin-induced prostacyclin production in rat aortic rings is mediated by protein kinase C.
G K Oriji, J E Tate, H R Keiser
Index: Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 55(5) , 309-13, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Endothelin (ET) is a vasoconstrictor peptide released from endothelial cells that is known to cause prostaglandin release. The mechanism remains unclear. To determine whether the protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathway is stimulated by endothelin, we pretreated rat aortic rings with either PKC activator or inhibitors and measured the release of prostacyclin (PGI2) by radioimmunoassay. ET (10(-9) M) produced a 10-fold increase in PGI2 release. Pretreatment with 10(-9) M of three different PKC inhibitors, 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)piperazine(CL), staurosporine, and 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyltmethyl)piperazine (H7), blocked ET-induced PGI2 release. ET-induced PGI2 release was also blocked by pretreatment with inhibitors of either phospholipase A2 7,7-dimethyleicosadienoic acid or trifluoromethyl ketone analogue) (10(-9) M) or cyclooxygenase (indomethacin) (10(-9) M). We conclude that ET activates PKC, which activates phospholipase A2, which liberates arachidonic acid, which increases PGI2 production and release.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
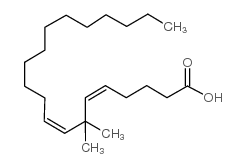 |
7,7-dimethyleicosadienoic acid
CAS:89560-01-0 |
C22H40O2 |
|
Exocytosis in chromaffin cells: evidence for a MgATP-indepen...
1994-05-15 [Biochem. J. 15 , 217-227, (1994)] |
|
Hyposmotically induced amino acid release from the rat cereb...
1999-10-09 [Brain Res. 844 , 1-9, (1999)] |
|
Discussion of the role of the extracellular signal-regulated...
2003-02-01 [Neurochem. Res. 28(2) , 319-26, (2003)] |
|
Phospholipase A2 is not responsible for lysophosphatidylchol...
1998-11-01 [Am. J. Physiol. 275(5 Pt 2) , H1782-7, (1998)] |
|
The effects of two phospholipase A2 inhibitors on the neurom...
1995-12-01 [Toxicon 33(12) , 1633-43, (1995)] |