Effects of yeast suspension density on the accumulation ratio of transported solutes.
A Kotyk
Index: Yeast 3(4) , 263-70, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The previously described effect of cell suspension density on metabolic and transport phenomena in yeast, apparently caused by inhibition by dissolved carbon dioxide, is also observed with the accumulation ratio of both sugars and amino acids where not only a kinetic but also a energetic factor comes into play. Unlike all previously measured metabolic and transport parameters, the dependence of the accumulation ratio on suspension density is not monotonic but shows a pronounced maximum in the range of 4-8 mg dry wt/ml, depending on yeast species and on cultivation conditions. In Rhodotorula gracilis and in Lodderomyces elongisporus it is not due to CO2 but is semiquantitatively related to the proton-motive force across the plasma membrane as well as to the intracellular ATP content. It is observed both in oxygen and in argon, over a wide range of pH values and of temperatures, but it is suppressed by metabolic inhibitors. It is expressed only in a range of transported solute concentrations between about 0.1 and 10 mM.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
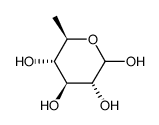 |
6-DEOXY-D-GLUCOSE
CAS:7658-08-4 |
C6H12O5 |
|
Murine Glut-1 transporter haploinsufficiency: Postnatal dece...
2009-01-01 [Neurobiol. Dis. 36 , 60-9, (2009)] |
|
Glucose-induced activation of rubidium transport and water f...
2001-01-01 [J. Exp. Bot. 52(354) , 99-104, (2001)] |
|
The O-polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Providen...
2005-05-23 [Carbohydr. Res. 340(7) , 1419-23, (2005)] |
|
Induction and characterization of an unusual alpha-D-galacto...
2007-01-30 [J. Biotechnol. 128(1) , 61-71, (2007)] |
|
Activation of adenylate cyclase in cdc25 mutants of Saccharo...
1993-03-22 [FEBS Lett. 319(3) , 237-43, (1993)] |