Incorporation of foreign compound metabolites into plant and soil constituents.
R C Honeycutt, I R Adler, G Boka, W L Secrest, B J Simoneaux, D D Sumner
Index: J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. 3(5-6) , 21-33, (1980)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Recent developments in the technology of removal and characterization of bound residues of two herbicides, nitrofen and profluralin, from plants and soil will be reviewed. 14C-Nitrofen was found to be metabolized into starch in wheat grain as well as bound into the lignin fraction of wheat straw. Profluralin and its metabolites were found to be bound to field aged soil in several ways probably including hydrogen bonding and covalent bonding. The bound metabolites of profluralin in soil could be categorized according to the type of bonding occurring as well as to the physicochemical characteristics of the bound pesticide. By assessing the type of bonding involved between pesticide and plants or soil, some assessment of the bioavailability of these bound residues to the environment can be made. When applied to tissues of food producing animals, these techniques would help release bound drug residues and provide technology for characterization of the released material.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
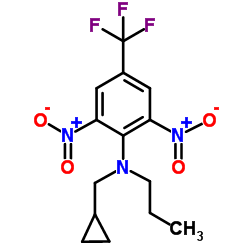 |
profluralin
CAS:26399-36-0 |
C14H16F3N3O4 |
|
Methodology for the determination of dinitroaniline herbicid...
1985-01-01 [J. Anal. Toxicol. 9(1) , 15-9, (1985)] |
|
In vitro anticryptosporidial activity of dinitroaniline herb...
1996-03-01 [FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 136(3) , 245-9, (1996)] |
|
Metabolism of profluralin in rats. 1. Identification of meta...
1988-01-01 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1(5) , 304-11, (1988)] |
|
Aerobic and anaerobic degradation of profluralin and triflur...
1980-01-01 [J. Environ. Sci. Health B 15(5) , 457-73, (1980)] |