| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
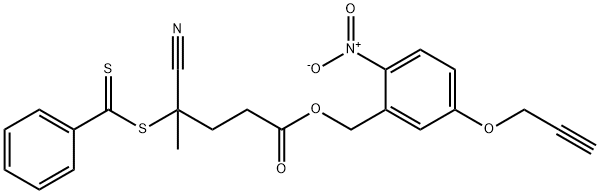 |
2-Nitro-5-(2-propynyloxy)benzyl 4-cyano-4- (phenylcarbonothioylthio)pentanoate
CAS:1318075-32-9 |
|
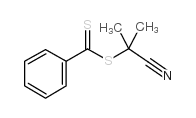 |
2-CYANOPROPAN-2-YL BENZODITHIOATE
CAS:201611-85-0 |