Sequence preference for strand cleavage of gapped duplexes by dynemicin A: possible mechanism of sequence-dependent double-stranded breaks.
T Kusakabe, M Uesugi, Y Sugiura
Index: Biochemistry 34(31) , 9944-50, (1995)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A double-stranded DNA cleavage mechanism by a novel enediyne type antitumor antibiotic, dynemicin A, has been investigated through sequence-dependent strand breakage of a series of duplexes containing a single nucleotide gap. We found that (1) dynemicin A breaks specifically at the 3'-shifted position by one base opposite the gap, (2) the strong cleavage is detected at 5'-Pu_Pu/3'-PyPuPy sequences, and (3) dynemicin H (aromatized form of dynemicin A) gives only a small inhibition effect (20%) on the cleavage of gapped duplex by dynemicin A. The long half-life of aromatization of dynemicin A (118 min, in the presence of DNA) obtained from HPLC analysis provides enough time for the second cleavage. The present results strongly indicate a two-step mechanism for the double-stranded DNA scission of dynemicin A. Namely, this double-stranded break is caused by two drug molecules, each of which cuts one DNA strand.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
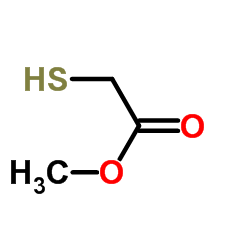 |
Methyl thioglycolate
CAS:2365-48-2 |
C3H6O2S |
|
Blood-brain barrier permeable gold nanoparticles: an efficie...
2014-12-29 [Small 10(24) , 5137-50, (2014)] |
|
Ligand-controlled growth of ZnSe quantum dots in water durin...
2012-09-11 [Langmuir 28(36) , 12931-40, (2012)] |
|
Simultaneous determination of dimethylarsinic acid and monom...
1999-01-01 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 13(5) , 350-3, (1999)] |
|
Thermochromism of heme adducts of Glycera hemoglobin and som...
1990-08-01 [J. Inorg. Biochem. 39(4) , 351-69, (1990)] |
|
Gold Nanorods Conjugated with Doxorubicin and cRGD for Combi...
2012-01-01 [Theranostics 2(8) , 757-68, (2012)] |