| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Phenylephrine hydrochloride
CAS:61-76-7 |
|
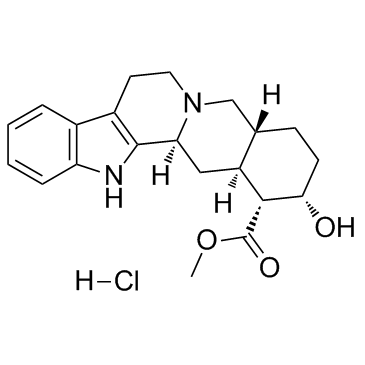 |
Yohimbine hydrochloride
CAS:65-19-0 |
|
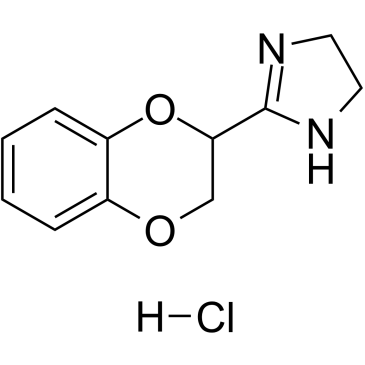 |
Idazoxan Hydrochloride
CAS:79944-56-2 |