Biological Chemistry Hoppe-Seyler
1991-06-01
Microbial metabolism of quinoline and related compounds. IX. Degradation of 6-hydroxyquinoline and quinoline by Pseudomonas diminuta 31/1 Fa1 and Bacillus circulans 31/2 A1.
G Bott, F Lingens
Index: Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 372(6) , 381-3, (1991)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Two strains, using 6-hydroxyquinoline as sole source of energy, carbon and nitrogen, have been isolated. These bacteria, designated 31/1 Fa1 and 31/2 A1, are also able to degrade quinoline. According to their physiological properties strain 31/1 Fa1 has been identified as Pseudomonas diminuta and strain 31/2 A1 as Bacillus circulans. 6-Hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline was found as intermediate in the degradation of 6-hydroxyquinoline and quinoline. 2-Oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline was the first metabolite in the degradation of quinoline.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
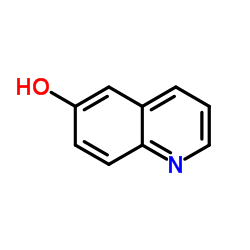 |
6-Hydroxyquinoline
CAS:580-16-5 |
C9H7NO |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Synthesis and antimosquito properties of 2,6-substituted ben...
2013-07-01 [Eur. J. Med. Chem. 65 , 295-303, (2013)] |
|
TDDFT study of the polarity controlled ion-pair separation i...
2014-07-15 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 128 , 280-4, (2014)] |
|
Excited-state prototropic equilibrium dynamics of 6-hydroxyq...
2010-11-08 [Chemistry 16(42) , 12609-15, (2010)] |
|
Excited state proton transfer in the Cinchona alkaloid cupre...
2010-10-21 [Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12(39) , 12562-9, (2010)] |
|
Excited-state proton transfer via hydrogen-bonded acetic aci...
2011-01-13 [J. Phys. Chem. A 115(1) , 19-24, (2011)] |