| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
3,5-dimethylpyrazole-1-carboximidamide hydrochloride
CAS:40027-64-3 |
|
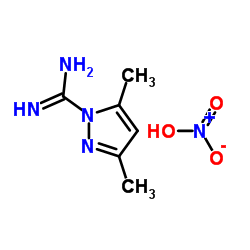 |
3,5-Dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-1-carboximidamide nitrate
CAS:38184-47-3 |