Biochemical characteristics and function of a fucosyltransferase encoded by ste7 in Ebosin biosynthesis of Streptomyces sp. 139.
Ming Chang, Li-Ping Bai, Jung-Jie Shan, Rong Jiang, Yang Zhang, Lian-Hong Guo, Ren Zhang, Yuan Li
Index: J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19(10) , 1092-7, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A novel exopolysaccharide named Ebosin was produced by Streptomyces sp. 139, with medicinal activity. Its biosynthesis gene cluster (ste) has been previously identified. For the functional study of the ste7 gene in Ebosin biosynthesis, it was disrupted with a double crossover via homologous recombination. The monosaccharide composition of EPS- 7m produced by the mutant strain Streptomyces sp. 139 (ste7(-)) was found altered from that of Ebosin, with fucose decreasing remarkably. For biochemical characterization of Ste7, the ste7 gene was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21. With a continuous coupled spectrophotometric assay, Ste7 was demonstrated to have the ability of catalyzing the transfer of fucose specifically from GDP-beta- L-fucose to a fucose acceptor, the lipid carrier located in the cytoplasmic membrane of Streptomyces sp. 139 (ste7(-)). Therefore, the ste7 gene has been identified to code for a fucosyltransferase, which plays an essential role in the formation of repeating sugars units during Ebosin biosynthesis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
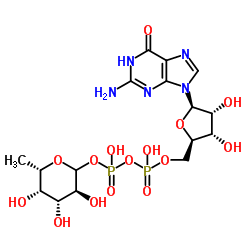 |
GDP-L-fucose disodium salt
CAS:15839-70-0 |
C16H23N5Na2O15P2 |
|
Low glucose depletes glycan precursors, reduces site occupan...
2015-07-01 [Biotechnol. J. 10 , 1051-66, (2015)] |
|
Chemo-enzymatic supported synthesis of the 3-sulfated Lewis ...
2008-04-07 [Carbohydr. Res. 343(5) , 970-6, (2008)] |
|
Structures of NodZ α1,6-fucosyltransferase in complex with G...
2012-02-01 [Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 68 , 160-168, (2012)] |
|
Two pathways for importing GDP-fucose into the endoplasmic r...
2010-02-05 [J. Biol. Chem. 285(6) , 4122-9, (2010)] |
|
Whole cell biosynthesis of a functional oligosaccharide, 2'-...
2012-01-01 [Microb. Cell Fact. 11 , 48, (2012)] |