Methylation and restriction endonuclease cleavage of linear Z-DNA in the presence of hexamminecobalt (III) ions.
G Soslau, J Parker, J W Nelson
Index: Nucleic Acids Res. 14(18) , 7237-52, (1986)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
These studies employed the synthetic linear DNA, poly dGdC, in the B and cobalt hexammine chloride (Co)-induced Z form to determine the effect of conformation on protein-DNA interactions. The rate of the reaction of the restriction endonucleases, Hha I and Cfo I, are reduced with Z DNA as compared to B DNA. The ability of both restriction endonucleases to react with an aggregate form of Z DNA (Z* DNA) is found to depend upon how the Z* DNA is formed. When Z* DNA is induced by low concentrations of Co (50 microM), the endonucleases remain active. In the presence of 100 microM Co, which causes increased aggregation, the endonucleases are inactive. The Hha I DNA methyltransferase reacts at equal rates with the B, Z and low cobalt Z* forms and at a greatly reduced rate with the high cobalt Z* form. These results are significantly different than those observed with Z form dGdC tracts inserted into circular DNA molecules.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
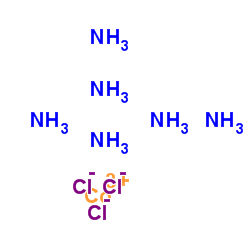 |
HEXAAMMINECOBALT(III) CHLORIDE
CAS:10534-89-1 |
H18Cl3CoN6 |
|
HCC ligation: rapid and specific DNA construction with blunt...
1986-12-22 [Nucleic Acids Res. 14(24) , 10118, (1986)] |
|
Iron regulatory element and internal loop/bulge structure fo...
1998-02-10 [Biochemistry 37(6) , 1505-12, (1998)] |
|
Protection of megabase DNA from shearing.
1995-10-11 [Nucleic Acids Res. 23(19) , 3999-4000, (1995)] |
|
The electron-transfer site of spinach plastocyanin.
1988-08-09 [Biochemistry 27(16) , 5876-84, (1988)] |
|
Reversible hypercondensation and decondensation of mitotic c...
2002-01-01 [J. Cell. Biochem. 85(2) , 422-34, (2002)] |