Teratogenicity of bifenox and nitrofen in rodents.
B M Francis
Index: J. Environ. Sci. Health B 21(4) , 303-17, (1986)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The teratogenicity of the diphenyl ether herbicide bifenox [2,4-dichlorophenyl 3'-carboxymethyl-4'-nitrophenyl ether] was compared to that of nitrofen [2,4-dichlorophenyl 4'-nitrophenyl ether] in rats and in mice. Neither compound increased prenatal mortality in mice. Because nitrofen causes both malformations that are compatible with survival to weaning and a high incidence of perinatal (but not of fetal) mortality, emphasis was placed on postnatal parameters of bifenox toxicity. In rats, bifenox caused a low incidence of "bloody tears", but it did not decrease survival to term or to weaning in rats or mice, and did not reduce Harderian gland weight in mice. Because the weight of the Harderian glands is a more objective measure of their status than is the presence of an eye discharge, it is concluded that bifenox is not teratogenic at the levels administered. Nitrofen decreased litter size, pup weight, and Harderian gland weight in mice.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
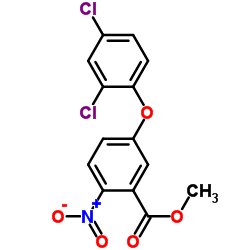 |
Bifenox
CAS:42576-02-3 |
C14H9Cl2NO5 |
|
Synthesis of aryl D-gluco- and D-galacto-pyranosides and 1-O...
1992-04-10 [Carbohydr. Res. 228(1) , 191-203, (1992)] |
|
Detection of mutagenicity of diphenyl ether herbicides in Sa...
1995-01-01 [Mutat. Res. 346(1) , 57-60, (1995)] |
|
Developmental toxicity of diphenyl ether herbicides in nestl...
1991-11-01 [J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 34(3) , 323-36, (1991)] |
|
Maternal and developmental toxicity of halogenated 4'-nitrod...
1999-02-01 [Teratology 59(2) , 69-80, (1999)] |
|
Genotoxic activity of the commercial herbicide containing bi...
1999-02-19 [Mutat. Res. 439(2) , 129-35, (1999)] |