Triosephosphate isomerases in Italian ryegrass ( Lolium multiflorum ): characterization and susceptibility to herbicides.
Daniele Del Buono, Bhakti Prinsi, Luca Espen, Luciano Scarponi
Index: J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(17) , 7924-30, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effect of treatments with four herbicides and a safener on the activity of triosephosphate isomerase (TPI) extracted from shoots of Italian ryegrass was investigated. It was found that atrazine and fluorodifen, herbicides which interfere with photosynthesis, caused a decrease in measured enzyme activity. In addition, the in vitro effect of oxidized glutathione (GSSG), a compound produced in situations of oxidative stress, on TPI activity was investigated. It was shown that GSSG was a strong inhibitor of enzyme activity, at low concentrations in a dose-time-dependent manner. The enzyme extracts were submitted to chromatographic purifications and to two-dimensional electrophoresis. Some spots had molecular masses ranging between 20 and 30 kDa and were characterized and identified by LC-ESI-MS/MS as TPIs. The mass spectrometry also made it possible to identify the presence of cysteine residues that could be subjected to S-glutathionylation, which regulate the enzyme activity.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
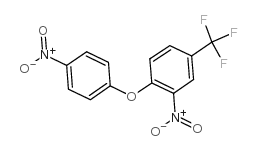 |
Benzene,2-nitro-1-(4-nitrophenoxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)
CAS:15457-05-3 |
C13H7F3N2O5 |
|
Induction of glutathione S-transferase in biofilms and germi...
2007-04-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73(8) , 2697-707, (2007)] |
|
Forced evolution of a herbicide detoxifying glutathione tran...
2003-06-27 [J. Biol. Chem. 278(26) , 23930-5, (2003)] |
|
Taxonomic distribution of plant glutathione S-transferases a...
2000-06-01 [Phytochemistry 54(3) , 267-73, (2000)] |
|
Crystallographic and functional characterization of the fluo...
2009-01-23 [J. Mol. Biol. 385(3) , 984-1002, (2009)] |
|
A comparative study on the interference of two herbicides in...
2011-11-23 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(22) , 12109-15, (2011)] |