Role of adenosine antagonism in the cardiorenal syndrome.
Mustafa M Dohadwala, Michael M Givertz
Index: Cardiovasc. Ther. 26(4) , 276-86, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF), generally related to signs and symptoms of volume overload, is one the most common reasons for hospitalization in the United States. Recently, it has been observed that the majority of patients with ADHF have baseline renal dysfunction. Moreover, heart failure (HF) treatment is limited by worsening renal function despite persistent volume overload. This connection between HF and renal dysfunction has been termed the cardiorenal syndrome and has made treatment of patients with stable and unstable HF challenging. Selective adenosine A1 receptor antagonists are novel pharmacologic agents that are currently under development to treat volume overload in HF while protecting or possibly improving renal function. In this article, we review the cardiorenal syndrome, the role of adenosine in renal function, and emerging data regarding the safety and efficacy of adenosine A1 receptor antagonists in patients with advanced HF.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
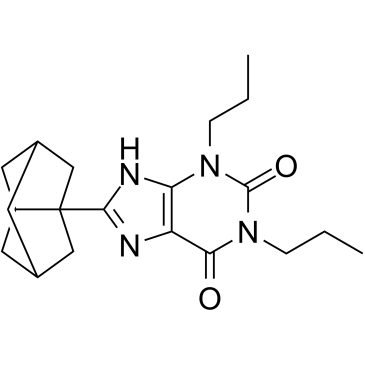 |
KW 3902
CAS:136199-02-5 |
C20H28N4O2 |
|
The effects of multiple doses of rolofylline on the single-d...
2010-01-01 [Am. J. Ther. 17(1) , 53-60, (2010)] |
|
The disconnect between phase II and phase III trials of drug...
2013-02-01 [Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 10(2) , 85-97, (2013)] |
|
Design and rationale of the PROTECT study: a placebo-control...
2010-01-01 [J. Card. Fail. 16(1) , 25-35, (2010)] |
|
Adenosine A2 receptor activation attenuates afferent arterio...
2007-10-01 [Hypertension 50(4) , 744-9, (2007)] |
|
Haemodynamic effects of rolofylline in the treatment of pati...
2010-11-01 [Eur. J. Heart Fail. 12(11) , 1238-46, (2010)] |