Removal of micropollutants from aerobically treated grey water via ozone and activated carbon.
L Hernández-Leal, H Temmink, G Zeeman, C J N Buisman
Index: Water Res. 45(9) , 2887-96, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Ozonation and adsorption onto activated carbon were tested for the removal micropollutants of personal care products from aerobically treated grey water. MilliQ water spiked with micropollutants (100-1600 μgL(-1)) was ozonated at a dosing rate of 1.22. In 45 min, this effectively removed (>99%): Four parabens, bisphenol-A, hexylcinnamic aldehyde, 4-methylbenzylidene-camphor (4MBC), benzophenone-3 (BP3), triclosan, galaxolide and ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate. After 60 min, the removal efficiency of benzalkonium chloride was 98%, tonalide and nonylphenol 95%, octocrylene 92% and 2-phenyl-5-benzimidazolesulfonic acid (PBSA) 84%. Ozonation of aerobically treated grey water at an applied ozone dose of 15 mgL(-1), reduced the concentrations of octocrylene, nonylphenol, triclosan, galaxolide, tonalide and 4-methylbenzylidene-camphor to below limits of quantification, with removal efficiencies of at least 79%. Complete adsorption of all studied micropollutants onto powdered activated carbon (PAC) was observed in batch tests with milliQ water spiked with 100-1600 μgL(-1) at a PAC dose of 1.25 gL(-1) and a contact time of 5 min. Three granular activated carbon (GAC) column experiments were operated to treat aerobically treated grey water. The operation of a GAC column with aerobically treated grey water spiked with micropollutants in the range of 0.1-10 μgL(-1) at a flow of 0.5 bed volumes (BV)h(-1) showed micropollutant removal efficiencies higher than 72%. During the operation time of 1728 BV, no breakthrough of TOC or micropollutants was observed. Removal of micropollutants from aerobically treated grey water was tested in a GAC column at a flow of 2 BVh(-1). Bisphenol-A, triclosan, tonalide, BP3, galaxolide, nonylphenol and PBSA were effectively removed even after a stable TOC breakthrough of 65% had been reached. After spiking the aerobically treated effluent with micropollutants to concentrations of 10-100 μgL(-1), efficient removal to below limits of quantification continued for at least 1440 BV. Both ozonation and adsorption are suitable techniques for the removal of micropollutants from aerobically treated grey water.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
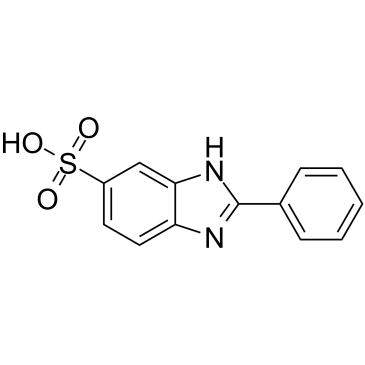 |
2-Phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonic acid
CAS:27503-81-7 |
C13H10N2O3S |
|
Sodium montmorillonite/amine-containing drugs complexes: new...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0121110, (2015)] |
|
Adverse reactions to sunscreen agents: epidemiology, respons...
2014-01-01 [Dermatitis 25(6) , 289-326, (2014)] |
|
Occurrence of xenobiotics in gray water and removal in three...
2010-09-01 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(17) , 6835-42, (2010)] |
|
Application of a biomimetic sensor based on iron phthalocyan...
[J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 21(7) , 1377-83, (2010)] |