1,4-Dioxane-2,5-dione-type monomers derived from l-ascorbic and d-isoascorbic acids. Synthesis and polymerisation.
Manuel Bueno, Inmaculada Molina, Juan A Galbis, Manuel Bueno, Inmaculada Molina, Juan A. Galbis
Index: Carbohydr. Res. 344(15) , 2100-4, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
l-Ascorbic and d-isoascorbic acids have been used as the starting materials for the preparation of (3R,4'S)-3-(2',2'-dimethyl-1',3'-dioxolan-4'-yl)-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione (IPTA), (3R and S, 4'S,6R)-3-methyl-6-(2',2'-dimethyl-1',3'-dioxolan-4'-yl)-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione (IPTP) and (3R,4'R)-3-(2',2'-dimethyl-1',3'-dioxolan-4'-yl)-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione (IPEA), three novel 1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione-type monomers. Ring-opening homopolymerisation and copolymerisation of the IPTA monomer, derived from l-ascorbic acid, with d,l-lactide have been performed. The polymers were characterised by elemental microanalysis, as well as IR and (1)H and (13)C NMR spectroscopies. GPC was used to estimate product molecular weights, and thermal studies (DSC and TGA) revealed that all the polymers were amorphous, being stable up to 250 degrees C under nitrogen.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
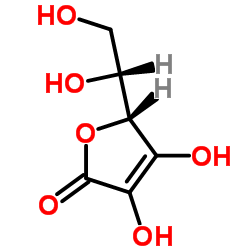 |
Erythorbic acid
CAS:89-65-6 |
C6H8O6 |
|
Effect of meat ingredients (sodium nitrite and erythorbate) ...
2013-09-01 [Food Microbiol. 35(2) , 108-15, (2013)] |
|
The effect of antibrowning agents on inhibition of potato br...
2012-11-01 [J. Food Sci. 77(11) , C1234-40, (2012)] |
|
Study on mitigation of acrylamide formation in cookies by 5 ...
2012-11-01 [J. Food Sci. 77(11) , C1144-9, (2012)] |
|
Determination of isoascorbic acid in fish tissue by hydrophi...
2010-07-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 397(6) , 2199-210, (2010)] |
|
NAD+-specific D-arabinose dehydrogenase and its contribution...
2006-11-27 [FEBS Lett. 580(27) , 6428-34, (2006)] |