| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
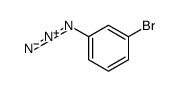 |
1-Azido-3-bromobenzene
CAS:2101-89-5 |
|
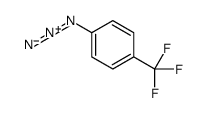 |
9-Azido-ααα-trifluorotoluene solution
CAS:5586-13-0 |
|
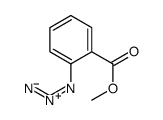 |
methyl 2-azidobenzoate
CAS:16714-23-1 |
|
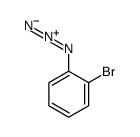 |
1-Azido-2-bromobenzene
CAS:3302-39-4 |
|
 |
1-Azido-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzene solution
CAS:1548-68-1 |
|
 |
methyl 3-azidobenzoate
CAS:93066-93-4 |
|
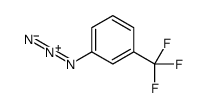 |
1-Azido-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzene solution
CAS:22001-17-8 |
|
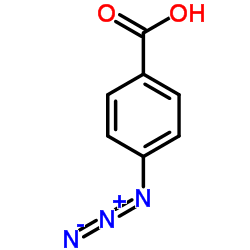 |
4-Azidobenzoic acid
CAS:6427-66-3 |