Cu2+ and Cu+ bathocuproine disulfonate complexes promote the oxidation of the ROS-detecting compound dichlorofluorescin (DCFH).
Hilde Laggner, Marcela Hermann, Bernhard M K Gmeiner, Stylianos Kapiotis
Index: Anal. Bioanal. Chem 385(5) , 959-61, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The water-soluble Cu+ chelator bathocuproine disulfonate (BCS) is widely used to quantify Cu+ or detect Cu+ formation in Cu2+-initiated oxidation reactions. The dichlorofluorescin (DCFH) assay is commonly used to monitor free radical reactions, reactive oxygen species (ROS), or reactive nitrogen species (RNS). Upon oxidation the non-fluorescent DCFH is converted into the fluorescent compound dichlorofluorescein (DCF). In the present communication we show that the Cu+ reagent BCS strongly facilitated the oxidation of DCFH in the presence of Cu2+ or Cu+. In contrast, 2,2'-dipyridyl (DP), which is also a Cu+-complexing reagent, but not as well known and therefore not as commonly used as BCS, did not cause any oxidative modification of DCFH in the presence of Cu2+ or Cu+. We therefore recommend that DP should be used instead of BCS to complex Cu+ in reactions which are initiated by Cu2+ and when ROS/RNS are analyzed by the DCFH oxidation assay.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
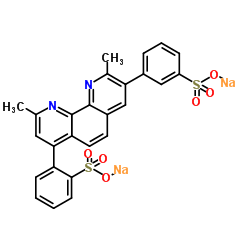 |
4,7-Diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline, 2,9-dimethyl disulfonate, disodium salt
CAS:52698-84-7 |
C26H18N2Na2O6S2 |
|
Leishmania amazonensis: inhibition of 3'-nucleotidase activi...
2015-08-01 [Exp. Parasitol. 131(1) , 63-8, (2012)] |
|
Ferroportin and exocytoplasmic ferroxidase activity are requ...
2013-06-14 [J. Biol. Chem. 288(24) , 17932-40, (2013)] |
|
Molecular insights into the metal selectivity of the copper(...
2009-04-21 [Biochemistry 48(15) , 3325-34, (2009)] |
|
Cu2+ is required for pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate to inhibit ...
2008-01-10 [Chem. Biol. Interact. 171(1) , 26-36, (2008)] |
|
Differential effects of cysteine and methionine residues in ...
2005-01-01 [Free Radic. Res. 39(1) , 15-20, (2005)] |