| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
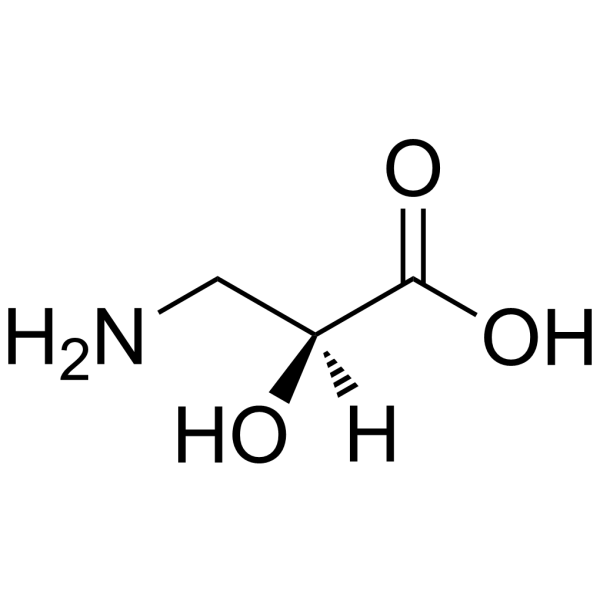 |
L-(-)-Serine
CAS:632-13-3 |
|
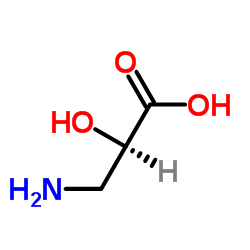 |
(2S)-3-Amino-2-hydroxypropanoic acid
CAS:632-11-1 |
|
 |
Isoserine
CAS:565-71-9 |