Analysis of skin lesions using laminar optical tomography.
Timothy J Muldoon, Sean A Burgess, Brenda R Chen, Désirée Ratner, Elizabeth M C Hillman
Index: Biomed. Opt. Express 3 , 1701-12, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Evaluation of suspicious skin lesions by dermatologists is usually accomplished using white light examination and direct punch or surgical biopsy. However, these techniques can be imprecise for estimating a lesion's margin or level of dermal invasion when planning surgical resection. Laminar optical tomography (LOT) is an imaging technique capable of acquiring depth-sensitive information within scattering tissues. Here, we explore whether LOT data can be used to predict the depth and thickness of pigmented lesions using a range of simulations and phantom models. We then compare these results to LOT data acquired on normal and malignant skin lesions in vivo.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
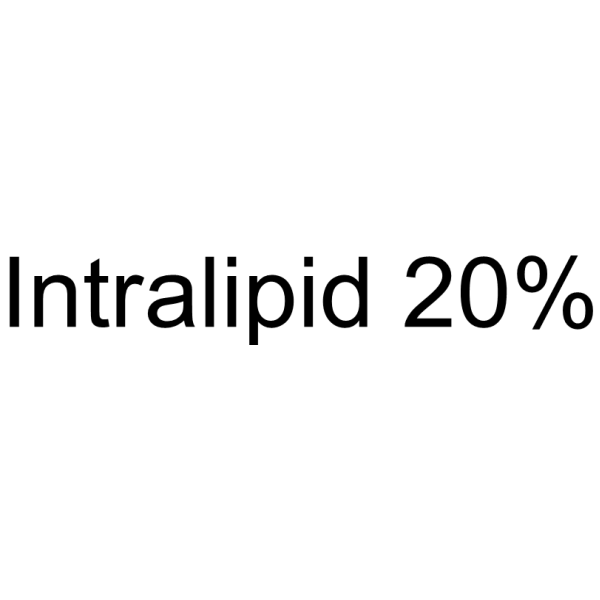 |
INTRALIPID
CAS:68890-65-3 |
C60H115NO10P |
|
Glucagon receptor antagonism induces increased cholesterol a...
2015-11-01 [J. Lipid Res. 56 , 2183-95, (2015)] |
|
Absorption of Intralipid and interferences from nutrients in...
1992-07-01 [Am. J. Surg. 164 , 45-50, (1992)] |
|
Effect of aging on anticonflict and CNS depressant activity ...
1987-01-01 [Psychopharmacology 93 , 443, (1987)] |
|
Counter-regulatory response to a fall in circulating fatty a...
2014-01-01 [PLoS ONE 9 , e113291, (2014)] |
|
In vivo microscopy of hemozoin: towards a needle free diagno...
2015-09-01 [Biomed. Opt. Express 6 , 3462-74, (2015)] |